Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) is a common and potentially serious condition that affects cats of all ages and breeds. It is one of the most common cat diseases and, as cat owners, understanding FLUTD is crucial for recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, treatment strategies, and prevention tips for FLUTD.
Understanding Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease FLUTD
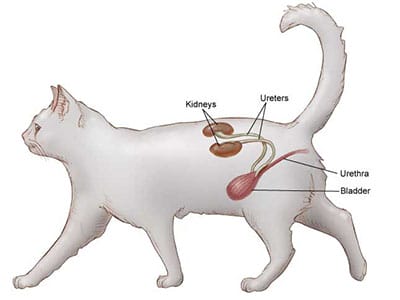
The feline urinary tract is a complex system consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. FLUTD encompasses a variety of urinary tract disorders, including urinary crystals, bladder inflammation (cystitis), and urinary blockages. Contributing factors may include diet, stress, inadequate hydration, and anatomical abnormalities.
Common Symptoms of Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease FLUTD
Recognizing the signs of FLUTD is essential for prompt intervention. Common symptoms include :
- frequent urination
- straining to urinate
- blood in the urine
- urinating outside the litter box
- signs of discomfort
- crying out while urinating
- excessive grooming of the genital area.
Diagnostic Procedures for FLUTD
Diagnosing FLUTD requires a thorough veterinary evaluation, which may include urinalysis, urine culture, imaging studies (such as ultrasound), and blood tests. These diagnostic procedures help identify underlying causes and guide appropriate treatment plans tailored to your cat’s specific needs.
Treatment Strategies for FLUTD
Treatment options for FLUTD aim to alleviate symptoms, address underlying causes, and prevent recurrence. Depending on the severity and nature of the condition, treatment may include dietary modifications, hydration therapy, pain management, and antibiotics to treat infections. Stress reduction techniques and environmental enrichment are also integral components of FLUTD management.
Prevention Tips for FLUTD
Prevention tips for Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) are crucial for maintaining optimal urinary health in cats. Here are some effective strategies to help prevent FLUTD:
- Hydration: Ensure your cat has access to fresh, clean water at all times. Encourage drinking by providing multiple water sources throughout your home, including water bowls and pet fountains. Consider adding water to your cat’s food or offering moisture-rich wet food to increase overall hydration.
- Dietary Management: Choose a high-quality cat food that supports urinary tract health. Look for options that are formulated to promote urinary pH balance and prevent the formation of urinary crystals or stones. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the most appropriate diet for your cat’s specific needs.
- Litter Box Maintenance: Maintain a clean and hygienic litter box environment to encourage regular urination and prevent litter box aversion. Scoop the litter box daily and completely change the litter on a regular basis. Provide multiple litter boxes in different areas of your home, especially in multi-cat households.
- Stress Reduction: Minimize stressors in your cat’s environment to reduce the risk of FLUTD flare-ups. Create a calm and predictable living space by providing hiding spots, vertical space for climbing, and quiet retreats. Consider pheromone diffusers or calming supplements to help alleviate anxiety in stressed cats.
- Environmental Enrichment: Stimulate your cat’s mind and body with interactive toys, puzzle feeders, and regular play sessions. Encourage physical activity and mental stimulation to promote overall well-being and reduce boredom-related stress.
- Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Schedule routine veterinary examinations to monitor your cat’s urinary health and detect any early signs of FLUTD. Your veterinarian can perform urinalysis, physical examinations, and other diagnostic tests to assess urinary function and identify potential risk factors.
- Observe Urinary Habits: Pay attention to your cat’s urinary habits and behaviors. Monitor litter box usage, urine output, and any changes in urinary patterns or litter box behavior. Seek prompt veterinary attention if you notice signs of discomfort, straining to urinate, blood in the urine, or other abnormalities.
Living with Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease : Tips for Cat Owners
As a cat owner, it’s important to be vigilant about your cat’s urinary health and observe any changes in behavior or litter box habits. Monitor urinary behavior closely, maintain open communication with your veterinarian, and seek prompt medical attention if you notice any concerning symptoms or changes in your cat’s condition.
Conclusion
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease (FLUTD) poses significant health risks for cats, but with proactive management and timely intervention, it can be effectively managed and controlled. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, treatment options, and prevention tips outlined in this guide, you can empower yourself to provide the best possible care for your feline companion.